A bull put spread is one of the simplest ways to generate options income without needing the market to rally. If you’ve ever asked “how do I trade a bull put spread safely?” or “why do professionals prefer bull put spreads over naked puts?”, this guide is for you.
At its core, a bull put spread lets you sell downside risk with a clearly defined maximum loss. You collect premium upfront, and as long as price stays above a chosen level, the trade works in your favour. That’s why I’ve used bull put spreads consistently for more than 15 years — especially on SPX — as part of a probability-based income approach.
In this guide, I’ll break down how bull put spreads work, when to use them, common mistakes beginners make, and the exact rules I follow for strike selection, risk control, and exits.
No hype, just a practical framework you can actually apply.
A bull put spread is a defined-risk options strategy where you sell a put option and buy another put option at a lower strike with the same expiration date. It generates a net credit and profits if the underlying asset stays above the short strike while limiting maximum loss.
Master the Bull Put Spread: Complete Learning Path
- Step 1: The Foundation: What are Bull Put Spreads? Understanding the core mechanics and risk-defined profile.
- Step 2: Strategy Selection SPX vs. SPY: Which is better for your account?: The tax and liquidity breakdown.
- Step 3: Tactical Execution Strike Selection Masterclass: How to find the sweet spot using Delta and Support.
- Step 4: Defensive Management The Pro Adjustment Guide: How to fix a trade when the market turns against you.
- Step 5: Advanced Setup Advanced SPX Setup & Examples: Real-world application and institutional workflows.
Understanding the Bull Put Spread: What It Is and Why It Works
A bull put spread is a type of credit spread created by selling one put option and buying another put option at a lower strike. Both options share the same expiration, which simplifies management.
I’ve used this strategy for years, especially in stable or mildly bullish markets. Instead of predicting a strong rally, I simply need the stock or index to remain above my short put strike — a far easier condition to meet than timing a directional move.
Breaking Down the Components
- Short Put (Sold Put): The higher strike you sell to collect premium.
- Long Put (Bought Put): The lower strike you buy to cap risk.
- Net Credit: Premium received minus premium paid — your maximum profit.
Bull Put Spread at a Glance
| Component | Meaning |
|---|---|
| Short put | Higher strike sold for premium |
| Long put | Lower strike bought for protection |
| Net credit | Maximum profit |
| Spread width – credit | Maximum loss |
| Short strike – credit | Breakeven price |
How A Bull Put Spread Makes Money
This strategy doesn’t require a rally — in fact, you can profit even if the stock moves sideways or slightly down. That’s why bull put spreads are considered high-probability income trades.
How the Numbers Work
- Breakeven: Short put strike − net credit.
- Max Profit: The credit received at entry.
- Max Loss: Spread width − credit received.
Example:
Sell $100 put for $3 → Buy $95 put for $1 → Net credit = $2.
If price stays above $100 → full profit.
If price drops below $95 → max loss = $3 (spread width $5 − $2 credit).
When to Use a Bull Put Spread
- Market is stable or slightly bullish
- Implied volatility is elevated (better premium)
- Price is above a strong support level
- You prefer defined risk over naked exposure
- You expect price to hold above a key level
Why I Prefer Bull Put Spreads Over Naked Puts
Naked puts offer more premium but expose traders to unlimited downside risk. A bull put spread defines risk upfront, requires less margin, and avoids catastrophic losses. This makes it accessible and safer for growing accounts — and it’s a core part of how I trade SPX inside my Monthly Trend service.
Comparison table: Bull Put Spread vs Naked Put:
| Feature | Bull put spread | Naked put |
|---|---|---|
| Risk | Defined and capped | Large and theoretically unlimited |
| Margin required | Lower | High |
| Max profit | Limited to credit received | Limited to premium received |
| Beginner suitability | High | Low |
| Account survivability | Much higher | Lower during market shocks |
Step-by-Step Guide to Placing a Bull Put Spread
- Select the Right Index (SPX preferred): Strong liquidity, tight spreads.
- Choose Strike Prices: Use support levels and probability/OTM distance.
- Pick Expiration: 2–6 weeks offers strong theta decay.
- Enter as a Single Credit Spread Order: Ensure risk-reward is attractive.
- Manage the Position: Close early or roll if price approaches your short strike.
Expanding the Strategy: Adjustments and Rolling
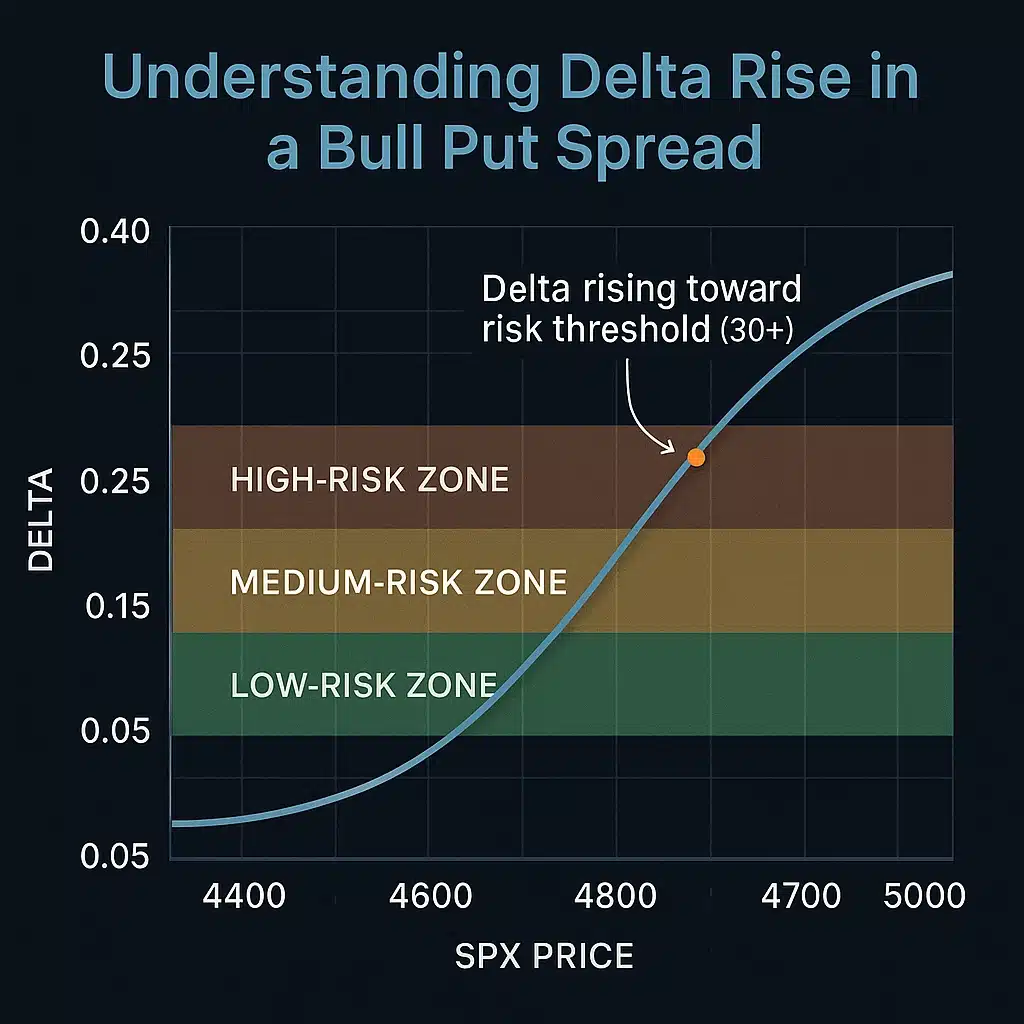
If price moves toward your short strike, you can:
- Close early for a smaller loss
- Roll out to a later expiration
- Roll down to safer strikes
Understanding adjustments separates consistent traders from emotional traders. If you want a full professional breakdown, see my guide:
How to Fix a Losing Bull Put Spread
Real-World Example
AAPL Trade Example:
- Sold 170 put for $3.00
- Bought 165 put for $1.50
- Net credit = $1.50 ($150 per contract)
If AAPL stayed above $170 → full profit.
If it dropped below $165 → max loss = $350.
Key takeaways
- Bull put spreads profit if price stays above a key level
- Risk is defined and capped from entry
- You don’t need a rally to make money
- Strike selection matters more than direction
- They are safer than naked puts for most traders
Final Thoughts: Why This Strategy Belongs in Your Toolkit
Bull put spreads are one of the most beginner-friendly ways to generate income with defined risk. Start small, focus on support levels, and use proper management. Over time, this strategy can become a consistent part of your trading system.
Bull Put Spread FAQs
What is the purpose of a bull put spread?
To generate income with defined risk by selling premium below the current price.
Is a bull put spread bullish or neutral?
It’s mildly bullish. You profit as long as price stays above the short put strike.
Why choose a bull put spread over a naked put?
Because your maximum loss is capped and margin requirements are smaller.
When should I avoid bull put spreads?
Avoid during earnings, major news events, or when implied volatility is extremely low.
Where should I place my short put strike?
Most traders choose a strike below support or where probability of ITM is under 20–25%.
How do you trade a bull put spread?
Sell a put below current price, buy a lower-strike put for protection, collect a net credit, and manage risk if price approaches the short strike.
Why use a bull put spread instead of buying calls?
Because you don’t need a rally. The trade works as long as price stays above your short strike.
What is the success rate of a bull put spread?
Many setups target a 60–75% probability of profit, depending on strike selection and volatility.
What are common mistakes with bull put spreads?
Oversizing, selling too close to price, trading through earnings, and ignoring support breaks.

